#Long 18th Century
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
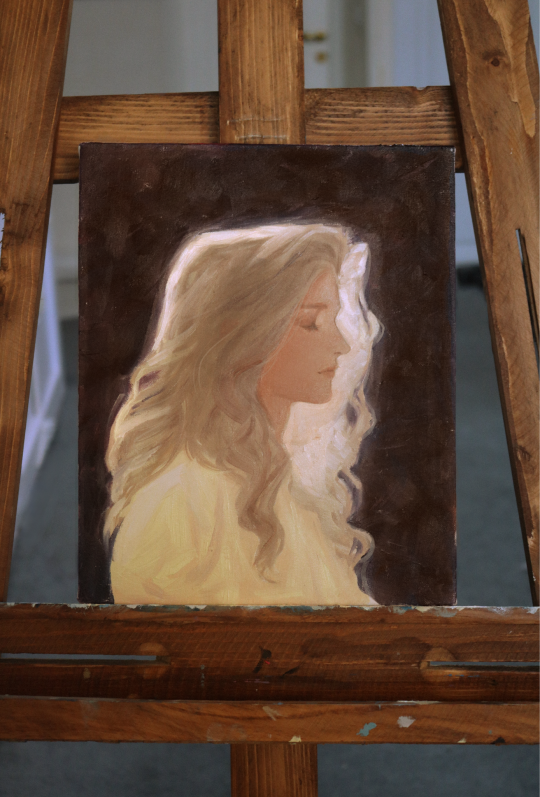

First time painting a portrait with oils so obv i chose Alucard to be my model <3
#You ever hyperfixate on a character so bad#you start painting them on a real fucijng canvas like you're an 18th century painter trying to recapture your long lost lover#art#my art#oil painting#alucard#castlevania#adrian tepes#adrian fahrenheit tepes
3K notes
·
View notes
Text
Normal 21st century people: wow that's cool!
My gremlin-ass brain: something something undress me! Hah!
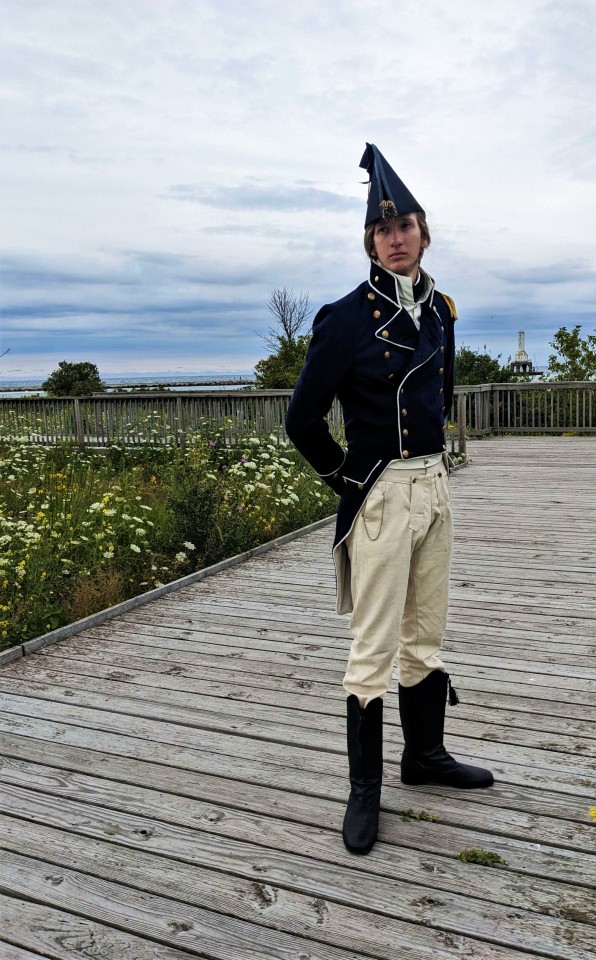

Royal Navy Commander Undress
Circa 1805
#hey sorry OP the joke wouldn't stop bothering me until I made it#I'll show myself out#“surely I'm not the only one turned on by olde timey military uniforms!”#she says while inhabiting the amrev tumblr community#which is adjacent to both frev and napoleonic tumblr#with a dash of austenite and dark academia tumblr#military uniform history#British military history#19th century#long 18th century#early 1800s
149 notes
·
View notes
Text
Utilization: By his anatomical peculiarities this dog is predestinated to puffin-hunting on the steep rocks around the fjords and along the shore.

The standard:
Neck: Clean-cut, of medium length, quite strong with a relatively well furnished collar.
Compendium comment:
The head is carried relatively low. The two last vertebrae (atlas/apsis) are shaped so that the dog can bend backwards so that the head touches the back. To do so is vital when turning in the narrow burrows. NB! This should NEVER be demonstrated the ring!

The standard:
Ears: Triangular ears of medium size, broad at the base, carried erect and very mobile. The cartilage of the ear lobe has the faculty of being able to retract itself so that the ear folds itself and flops in a specific manner, either backwards or in right angle upwards, so as to close the auditory passage.
Compendium addition:
The ears of the Lundehund have a unique muscle that enables them to fold and close the ears when entering the burrows, thus protecting them against dirt and moisture. The turning and folding of the ears probably also is help in locating the birds.
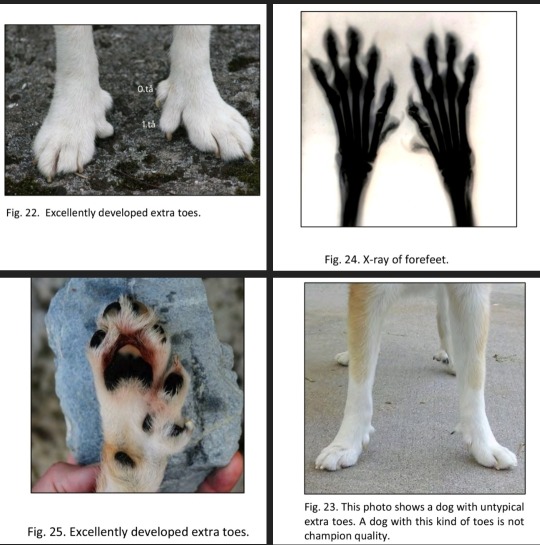
The standard:
Forelimbs: Moderately angulated. Forearm: Straight.
Forefeet: Oval shaped, turning slightly outwards, with at least six toes of which five must rest on the ground. Eight pads on each foot. The two inner toes, formed respectively by 3 and 2 phalanges and endowed with a ligamentary and muscular system, make the foot look solid.
Compendium addition:
Very flexible and elastic shoulder muscles. The Lundehund has joints that allow the forelimbs to extend at nearly 90 degrees from the body, but this must NEVER be demonstrated in the ring! The forefeet turn slightly outwards to give room for the extra toes.
The Norwegian Lundehund is a polydactyl. Instead of the normal 4 digits, the Lundehund normally has 6 digits, all fully formed, jointed and muscled, with tendons going up the inside of the leg, partly responsible for its wide front gait. Some specimen may have more, others less than 6 digits per foot, but less than 6 on front feet should lead to downgrading. The extra toes help the dog climbing up and down crevices in screes and cliffs.
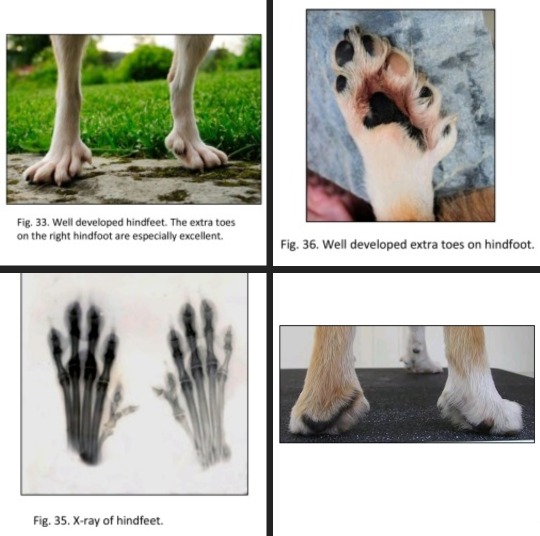
The standard:
Hindfeet : Oval shaped, turned slightly outwards, with at least six toes - four of which must rest on the ground. Seven pads on each foot, the one in the middle, the most important one by its size, being attached to the inner pads corresponding to the two inner toes. When the dog is standing up on a flat surface, the weight of the body must be evenly distributed on the pads.
Compendium comment:
More than 6 digits is not a fault. 5 digits are acceptable on the hind feet. The extra toes on the hind feet are normally less developed than those on the forelegs and variations from the ideal, both regarding number and placement, should not be penalized.
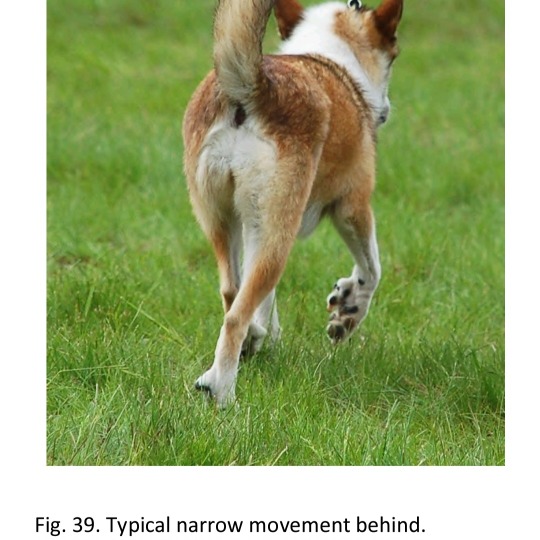


The standard:
Gait/Movement: Light and elastic. An external rotary action of the forelegs and somewhat close action behind is characteristic of the breed.
Compendium comment:
In judging the movements of the Lundehund, one must consider that this dog is built to climb efficiently up and down steep cliffs and screes. The extra pads on both fore- and hind paws must then touch the surface to aid the dog in climbing. The extra toes help getting a grip, both in ascent and descent. The wide front with extra flexibility enables climbing safely up and down crevices, as the forelegs can grip at a 90 degrees angle to the body. On flat surfaces, the Lundehund will show typical rotating front movements, due to tendons and muscles from the extra digits on the inside of the legs. Hind movements are narrow.
#norwegian lundehund#lundehund breed compendium#(excerpts)#photos from the compendium + the top from a veterinary journal on outcrossing#is2g every time i talk about this breed it sounds like youre making a fantasy species thats a Dog But Slightly Off#long post#some of these traits appear in other primitive breeds as well#lundehunds were described in 17th and 18th century texts. but we know there have been dogs in this area for thousands of years#plently long enough to produce a freak of nature (<3)
995 notes
·
View notes
Text






#historical fashion#fashion#historical#history#historical clothing#historical dress#long dress#textiles#dress#high fashion#old fashioned#victorian#19th century fashion#18th century fashion#1800 fashion#1700s fashion
669 notes
·
View notes
Text
Early 18th (and late 17th) century fashions are so under-utilized in vampire media and I think it's a damn shame.
I don't actually think I've ever seen a single image of a vampire character in an early 18th century suit. Hardly any movies set in that era either, and hardly any historical costumers who do it. (Even my beloved gay pirate show set in 1717 takes nearly all of its 18th century looks from the second half of the century. Not enough appreciation for baroque fashion!!)
Yes I love late 18th century fashion as much as anyone, and 19th century formal suits are all very well and good, but if you want something that says old, dead, wealthy, and slightly dishevelled, then the 1690's-1730's are where it's at.
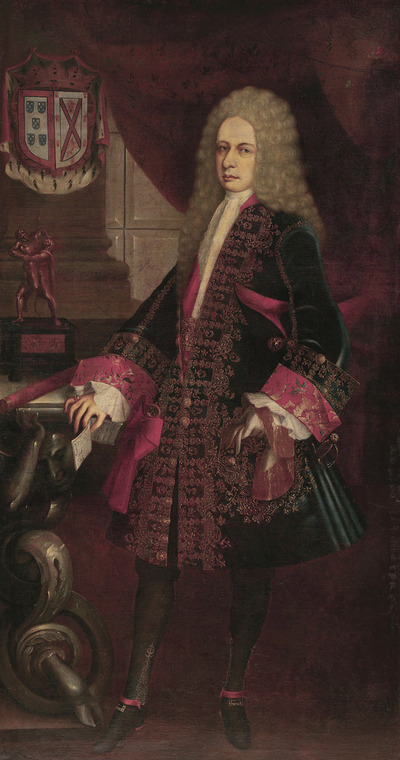

(Retrato del Virrey Alencastre Noroña y Silva, Duque de Linares, ca. 1711-1723.)
There was so much dark velvet, and so many little metallic buttons & buttonholes. Blood red linings were VERY fashionable in this era, no matter what the colour of the rest of the suit was.
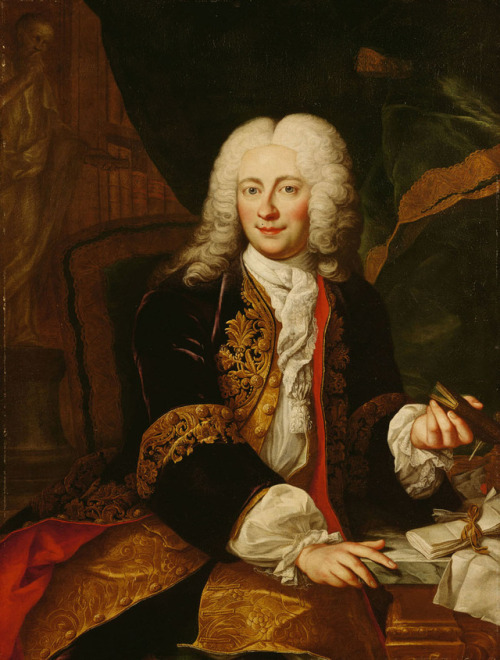

(Johann Christoph Freiherr von Bartenstein by Martin van Meytens the Younger, 1730's.)
The slits on the front of the shirts are super low, they button only at the collar, and it's fashionable to leave most of the waistcoat unbuttoned so the shirt sticks out, as seen in the above portraits.
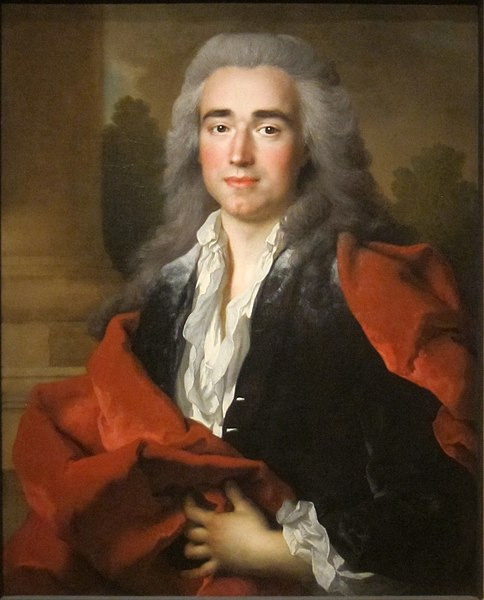

(Portrait of Anne Louis Goislard de Montsabert, Comte de Richbourg-le-Toureil, 1734.)
Waistcoats are very long, coats are very full, and the cuffs are huge. But the sleeves are on the shorter side to show off more of that shirt, and the ruffles if it has them! Creepy undead hands with long nails would sit so nicely under those ruffles.
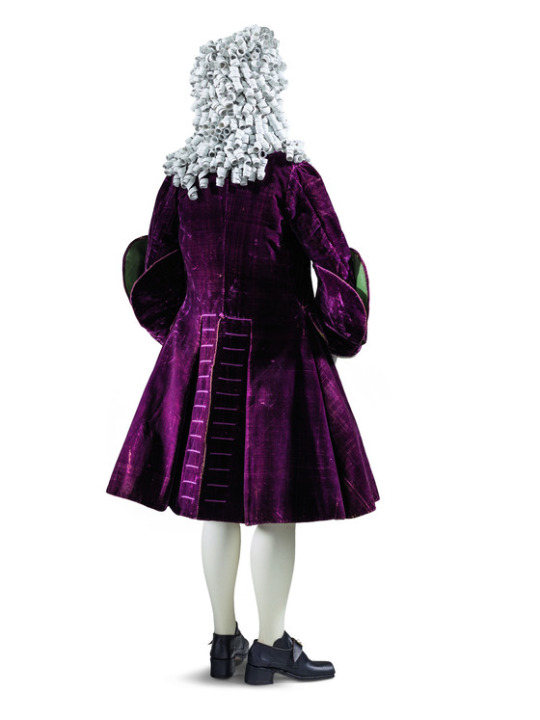
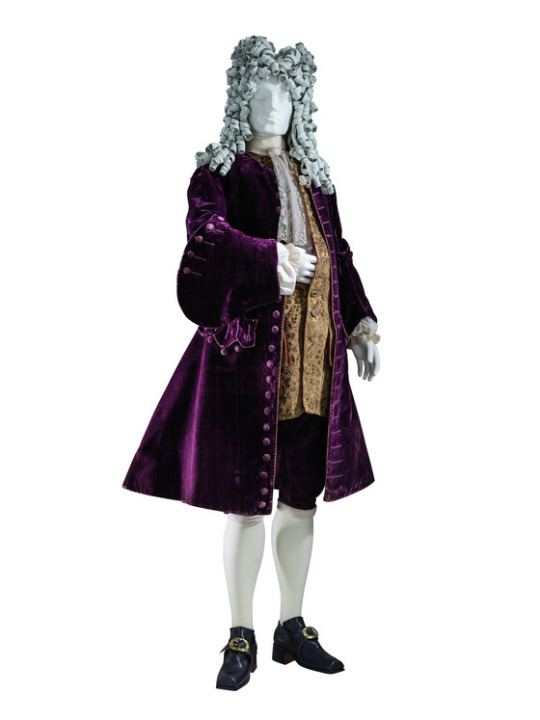


(1720's-30's, LACMA)
Embroidery designs are huge and chunky and often full of metallic threads, and the brocade designs even bigger.
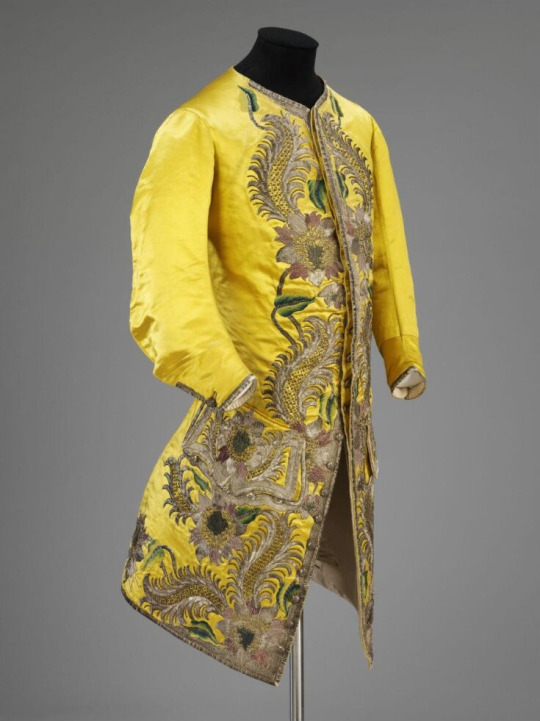

(1730's, V&A, metal and silk embroidery on silk satin.)
Sometimes they did this fun thing where the coat would have contrasting cuffs made from the same fabric as the waistcoat.
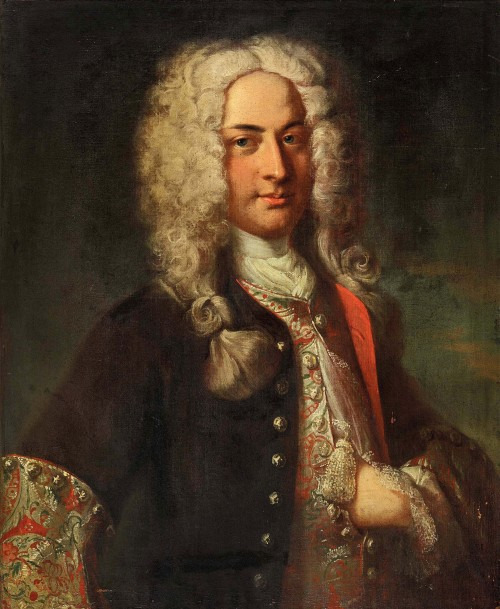

(Niklaus Sigmund Steiger by Johann Rudolf Huber, 1724.)
Tell me this look isn't positively made for vampires!
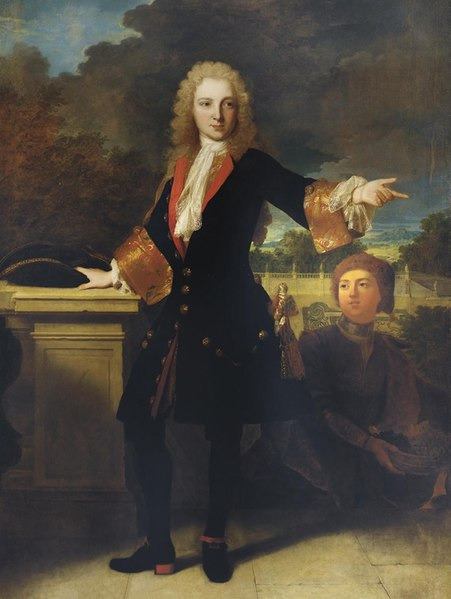

(Portrait of Jean-Baptiste de Roll-Montpellier, 1713.)
(Yeah I am cherry-picking mostly red and black examples for this post, and there are plenty of non-vampire-y looking images from this time, but you get the idea!)
And the wrappers (at-home robes) were also cut very large, and, if you could afford it, made with incredible brocades.
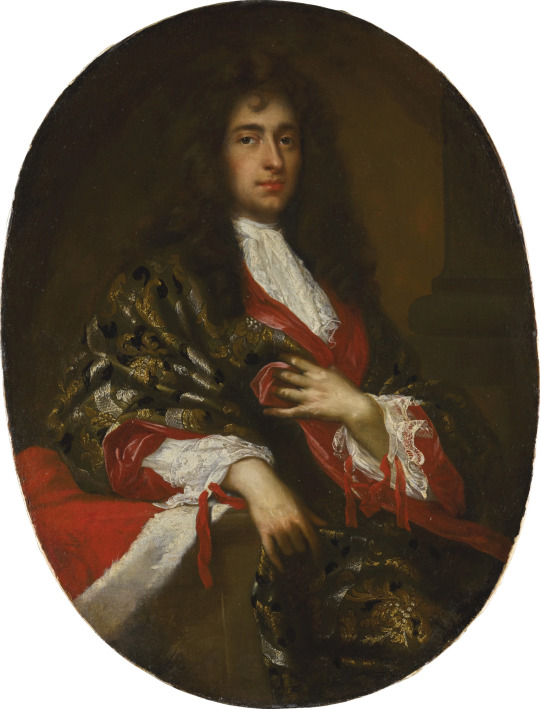

(Portrait of a nobleman by Giovanni Maria delle Piane, no date given but I'd guess maybe 1680's or 90's.)
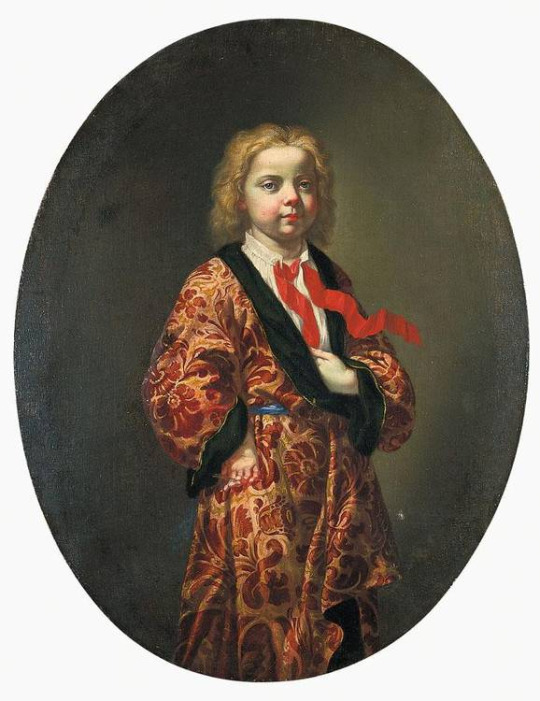

(Circle of Giovanni Maria delle Piane, no date given but I'd guess very late 17th or very early 18th century.)
Now that looks like a child who's been stuck at the same age for a hundred years if I ever saw one!
I don't know as much about the women's fashion from this era, but they had many equally large and elabourate things.
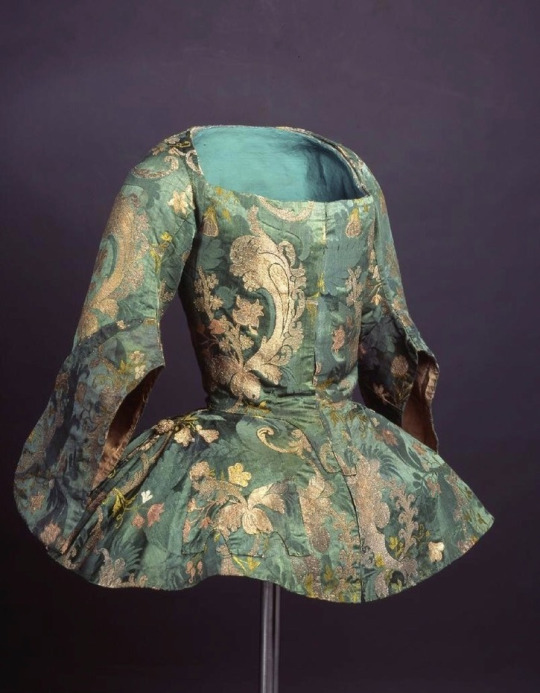

(1730's, Museo del Traje.)
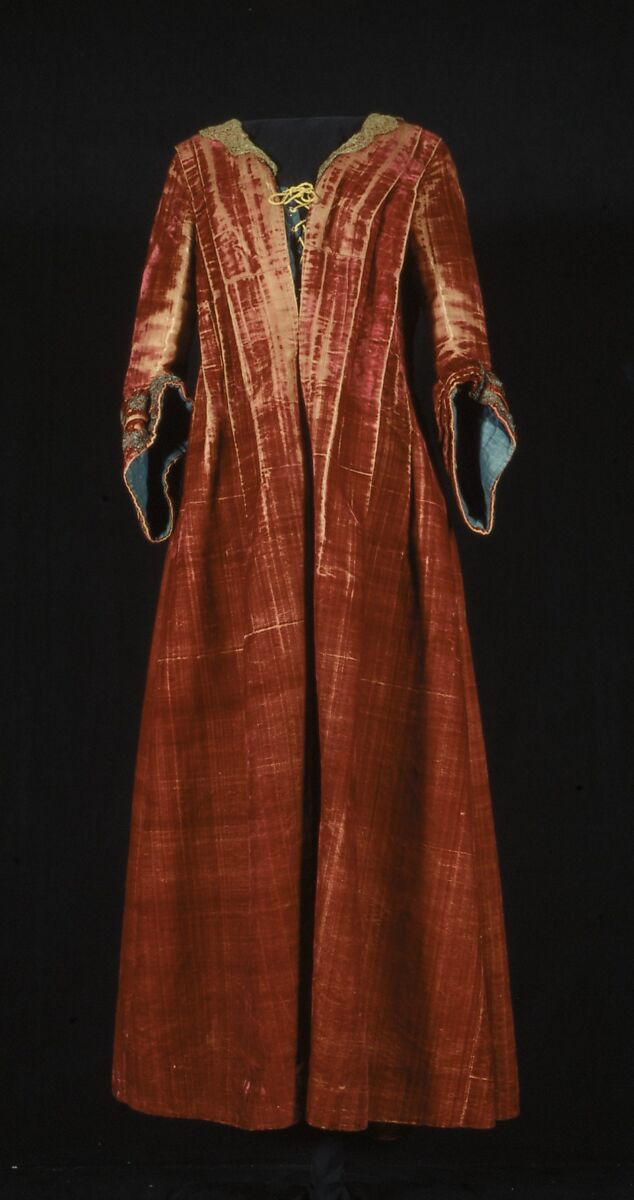

(Don't believe The Met's shitty dating, this is a robe volante from probably the 1720's.)
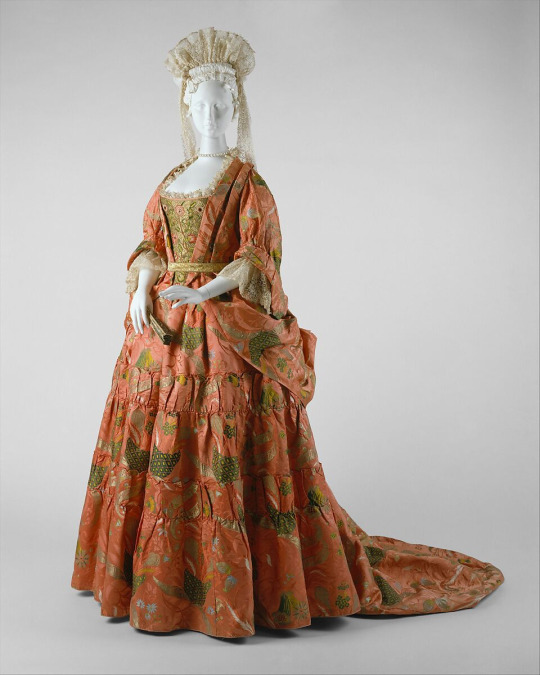
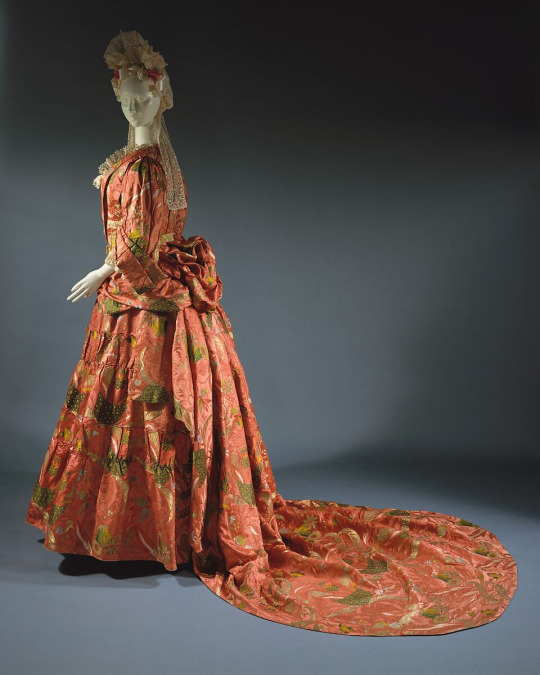


(Mantua, c. 1708, The Met. No idea why they had to be that specific when they get other things wrong by entire decades but ok.)
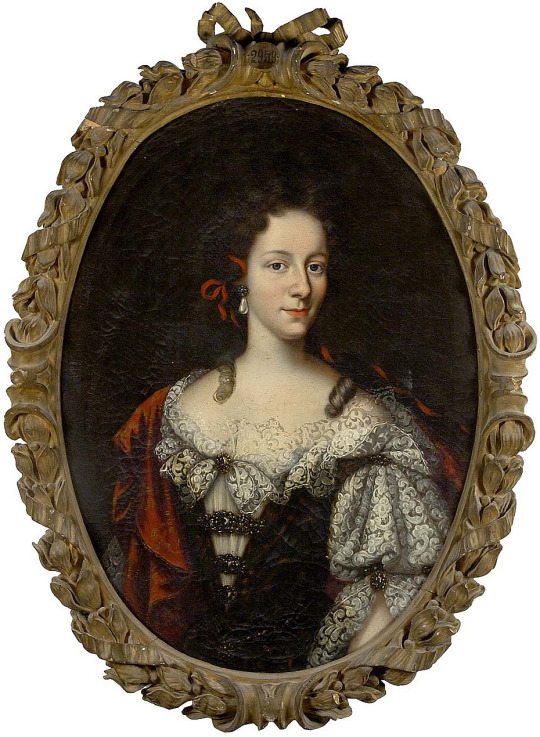

(Portrait of Duchess Colavit Piccolomini, 1690's.)
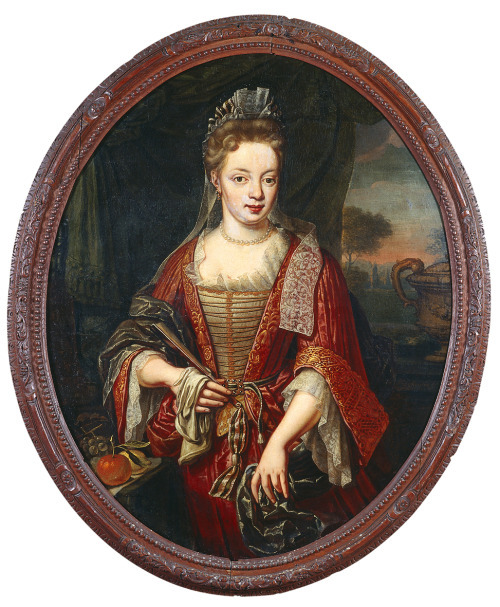

(Maria van Buttinga-van Berghuys by Hermannus Collenius, 1717.)
Sometimes they also had these cute little devil horn hair curls that came down on either side of the forehead.
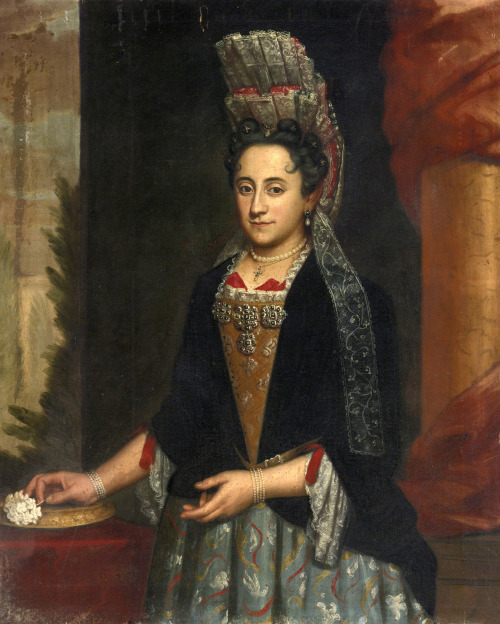

(Viago in drag Portrait of a lady, Italian School, c. 1690.)
Enough suave Victorian vampires, I want to see Baroque ones! With huge wigs and brocade coat cuffs so big they go past the elbow!
#long post#vampires#fashion#history#18th century#17th century#someday. SOMEDAY I will make a black/red/dark orange/metallic gold 1720's suit#I've got nearly all the materials I just need to:#1. Learn how to make early 18th century metallic thread buttons‚ preferably without having to buy the super expensive kind of thread#2. get a wig and style it appropriately
3K notes
·
View notes
Text






In any case it seems that Maria Theresa had expected a daughter. One of her courtiers, Count Dietrichstein, wagered against her that the new baby would be a boy. When the appearance of a girl, said to be as like her mother as two drops of water, meant that he had lost the bet, the Count has a small porcelain figure made of himself, on his knees, proffering verses by Metastasio to Maria Theresa. He may have lost his wager but if the new-born augusta figlia resembled her mother, then all the world would have gained.
Marie Antoinette: The Journey - Antonia Fraser
#marie antoinette#maria theresa#18th century#house of habsburg#austria#house of habsburg lorraine#long live the queue#pretend that's little antoine there ok :P
71 notes
·
View notes
Text
my one toxic trait is that I vastly overestimate the extent to which an average person wants to hear about 18th century philosophers' sex lives
#if you talk to me long enough you're bound to get an impromptu lecture#don't mean for it to happen it just kind of does#philosophy#philosophy memes#history memes#history shitposting#1700s#18th century#me coded#rousseau#diderot#voltaire#could go on probably
127 notes
·
View notes
Text

I usually don't post wips so openly like this but I have an idea.
What if canon Ace, after marineford, is isekaied to an old-fashioned, coloniser England? He wakes up confused like what the God-fuck happened and it just so happens that he ends up in a noblefamily's courtyard where he meets their youngest son who's his age who reminds him a bit too much of someone very familiar. The guy's name is Sabo too.
As of writing this, the fic is still a nebulous mess in my head but here's what I have.
Ace's immediately interested. The moment he went up to the study to ask for help, everyone just screams how indecent he is because he's shirtless and very attractive. The women blush, which Ace, being a greasy player to some extent, doesn't mind, but then there's Sabo who blushes in the same way. The neurons started activating in his mind. Ace never did it with guys too often but hey, he nearly died! He'll figure it out! Let's Fucking Go!
Sabo's also interested in this sense, "H-how rude! Who's this naked imbecile (Ace's just wearing his iconic shorts and boots)? Is he mad? In this weather? (looks down. Blushes immediately) That's a rather... large... scar........ What kind of w-warrior is he? Where is he from? Roman soldiers were known for being handsome, is he... (he can't believe himself for looking at his tits again) Why is he looking at me? His hair is too long for a man. (Sabo sees his smoky black eyes once more and turns away, out of breath) He's the Devil himself. I refuse to give in to temptation. I r-refuse to sin. I refuse!"
It doesn't end there, though. This hunk of a man gets thrusted to Sabo's care because no one trusts women to keep it in their pants if the Portgas D. Ace with his infinite, maxxed out rizz is right here. Sabo wants to cut his hair but couldn't bring himself to because it's just too beautiful. He simply cuts the fringe and dry-ends off before forcing Ace to shower and change into more appropriate clothing, aka this multi-layered suit that Ace wore wrongly.
Sabo couldn't stop himself from laughing. Ace pouted so much like a grumpy cat. Sabo started coughing and wiped his eyes.
"Why'd you stop?" Ace said. "Laugh more. I don't mind 'cause you're so cute."
Sabo finally sobered up. What was he doing? Acting like some lovesick fool. He never acted that way towards his own fiancé...
He didn't say anything as he helped Ace wear it properly. He couldn't help but feel he's doing something wrong. Ace looked so uncomfortable but it seemed that he understood why he's wearing this. Sabo hid his smile when Ace sneezed. Maybe he wasn't so bad.
When he's done, Sabo thought... Well, Ace is still handsome but he felt like he had taken something away from him, the thing that made him so special to begin with: his freedom. There's some spite in Sabo's grimace.
Sabo never had the chance to even dream of freedom.
#acesabo#saboace#portgas d ace#revolutionary sabo#jacqueline's writing wips#my art#istg THIS will be the next long form fic#i want to try my hand at incorporating some irl history#thanks hetalia you bastard#i want lots of dramatic yearning#it'll be very fun for ace to drop random shit like yeah i went to a skyisland and sabo's like ??? Are You Mad?#oh imagine ace telling sabo he's a pirate casually in chapter 2#SABO WOULD LOSE HIS SHIT AND STRANGLE HIM FR#AH THIS IS SO FUN TO THINK ABOUT#and sabo falling in love with ace fr because he's just everything sabo and this world isnt#fun adventurous free kind beautiful#and ace falls for sabo too the more he accepts that this isnt his childhood bestie but a different person#nobleman sabo is smart and strict but he's just so curious that ace wants to show him everything he wants to know!!!#mutual pining ftw!#including gay sex lmao#for my reference this takes place in the 18th century#jacqueline's ace isekai au
61 notes
·
View notes
Note
Hyper niche question for my autism warrior: What was the perception of aide-de-camps during the AmRev like? I assume it would be viewed as a softer position - though of course, the extent would vary depending who your CO was - but many did see action and a few were reassigned so they could fight
Hey y’all… how y’all doing… i know its been yet another period of many moons since ive posted or answered (i hope this information is still relevant btw), but ive had a lot going on with getting a job, finding colleges, my mommy issues, travel, etc. anyway, im back, and im here to tell you about my main men
It actually was not viewed as a softer position at all! The station of aide-de-camp was highly desirable for several reasons, which i will describe approximately right now
1) people had to compliment you a LOT to get in
Most of the results I got from my research on this ask were letters of recommendation for potential aides-de-camp. Letters of recommendation were high honors for any station, especially for that of a military capacity. According to my favorite source on the American Revolution (which you should know by now), George Washington’s Indispensable Men by Arthur S. Lefkowitz, it was practically impossible to get a job as an aide-de-camp if you did not have a widely positive reputation or a letter of recommendation from someone reputable (or both if you wanted to clerk for the Commander-in-Chief).
I found one letter of recommendation from j*hn ad*ms that i think serves as a very good example of the sort of statements that could land you a seat at a Continental officer’s writing desk:
“There is another Gentleman of liberal Education and real Genius, as well as great Activity, who I find is a Major in the Army; his Name is Jonathan Williams Austin. I mention him, sir, not for the Sake of recommending him to any particular Favour, as to give the General an opportunity of observing a youth of great abilities, and of reclaiming him from certain Follies, which have hitherto, in other Departments of Life obscurd him.”
-John Adams to George Washington, June 19-20, 1775, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (Founders Online, Washington Papers)
Those are my italics btw. These compliments are carefully chosen to suit the honor culture that was so pervasive throughout the 18th century and first half of the 19th century. A liberal education at the time was very hard to come by, and would be of great importance in a clerical position. Great activity also helps, because you dont want some lazy ass writing to Congress under your name, or god forbid George Washington himself, you might get hung (not really). The mention of youth is also intentional, since young men have always been preyed upon by the military. I think it’s especially noteworthy the final phrase of “reclaiming him from certain Follies”, which indicates that he might have previously had a negative reputation- whether it was warranted or not, im not sure.
2) the pay was fucking fire
For this we’re going to be utilizing my super amazing math scores that im renown for throughout the math community (yall dont know about my math tumblr), and we’re going to be using Alexander Hamilton as our lab rat, as per usual.
Alexander Hamilton joined Washington’s staff in early 1777 where a regular aide-de-camp (not a military secretary) made $33 dollars a month, which averages to about $1.10 a day. Meanwhile, according to the University of Missouri, the highest paid laborer in Massachusetts in the same year made $0.50 a day, which is about $15 a month, others making as little as about $0.22 a day, so around $7 a month. If you’re looking for ratios, by the end of the war, a pound of raisins was around $0.30. So, the highest paid Massachusetts laborer could save up every paycheck from 1777 to 1782 and buy 324 pounds of raisins, and Alexander fucking Hamilton could waltz up next to him and buy 712.8 pounds of raisins and rub it in his sad, poor face. And he wouldn’t even share because he was a congressman by that time and congressmen HATE THE POOR.
Disclaimer: Hamilton’s numbers dont include the time he quit the office bc I didn’t feel like googling how long he was away for and also i dont care. And yeah he probably would share his raisins with the guy, Hamilton was pretty nice, but i dont think he’d buy 712.8 pounds of raisins in Massachusetts anyway. Or maybe he would, I dont fucking know, stop asking me questions
3) it gave you a lot of street cred
There are many instances of aides-de-camps rising to higher status after their service, but i dont give a fuck about those nerds going into politics and law and stuff.
Most people now only know about Washington’s aides (or if you’re really autistic you know Lafayette’s too), but at the time, being an ADC to any general would get you fairly well known in society. General Sullivan’s aides seem to have been pretty well known and admired, as they are frequently mentioned in John Adams’ correspondence with other congressmen, as well as that of Benjamin Franklin with French diplomats all the way across the Atlantic.
But I imagine you’re also wondering (or at least i am) about what the everyday enlisted man thought of the ADCs, and that answer doesn’t really change. Of course, the men sitting out in the rain and mud without food for the past week are going to be envious of the guys who get to sleep in a house, but their quarters weren’t the most comfortable either. Aides-de-camp were probably the most connected out of the disconnected officers, if that makes sense. They weren’t fraternizing with the enlisted, but they were seen by them more frequently than the generals, and they were the ones advocating for the needs of the enlisted men. Even if they didn’t have any battle experience whatsoever (which really was never the case, i cant think of an aide who WOULDNT have seen battle), they would still be respected by the men as hardworkers and the only people who might actually get them food and clothes.
Thank you for the ask! I really enjoyed researching it and my family had a great time joking about me hunched over my ipad reading through the national archives while we all watched jeopardy, misspelling like every other word because its hard to type on an ipad. Im going to try to be more active, so please feel free to send further questions! I forgot how cathartic research is for me so id be very happy to do more. I have one more ask in my inbox i’ll try to get done sometime in the next few days. Love yall!
#history#alexander hamilton#amrev#american history#asks#american revolution#18th century#1700s#hamilton#washington’s aides#aides de camp#tench tilghman#john laurens#richard kidder meade#benjamin tallmadge#john adams#btw if you cant tell i totally forgot my old post format#i dont even want to know how long its been since my last post#dont tell me#if i ignore it it didn’t happen#publius originals
45 notes
·
View notes
Text
me trying to convince myself i care about menswear for a second so i can design an outfit for a male character
#i really cant be bothered#late 18th century is the closest i get to liking male fashion#at least they had long hair for a second?
31 notes
·
View notes
Note
I would absolutely love to see examples of historical terminology? I feel like I've only scraped the surface.
So I'm going to focus mostly on 18th century English because that's what I read the most (we will dip a little into French but mostly from an English perspective). Even narrowing the focus there's still kind of a lot. Like I'm probably going to forget something cause there is so much to talk about.
Sexuality
The first thing that's important to understand is sexuality labels were action based not attraction based. This doesn't mean people didn't understand sexual attraction, they very much did, it's just that terminology was based on action not attraction. Terminology was essentially separated into men who have sex with men and women who have sex with women. It also important to remember that these terms were not exclusive to men who only had sex with men and women who only had sex with women but also applied to people who had sex with both men and women.
Men Who Had Sex With Men
Sodomy/Buggery
The terms most commonly used in formal/legal contexts were sodomite and bugger. Bugger comes from buggery and sodomite from sodomy, both of which broadly speaking referred to anal intercourse or bestiality regardless of sex/gender but was most commonly associated with sex between men. The legal definition of sodomy in English common law was as follows:
Sodomy is a carnal Knowledge of the Body of Man or Beast, against the Order of Nature; It way be committed by Man with Man, (which is the most common Crime) or Man with Woman; or by Man or Woman with a Brute Beast. Some Kind of Penetration and Emission is to be proved, to make this Crime, which is Felony both by the Common and Statute Law, in the Agent and all that a present, aiding and abetting; also in the Patient consenting, not being within the Age of Discretion.
~ The Student’s Companion or, the Reason of the Laws of England by Giles Jacob, 1734, p239
However colloquially it was generally used to describe sex between men without the focus on Penetration and Emission.
Related to sodomy were the words sodomitical, sodomitically and sodomiting, these terms were used to describe a person, action or place that was related to sodomy (esp. sex between men) but did not necessarily constitute legal sodomy. (for examples see Trial of Martin Mackintosh, 11 July 1726, A Treatise of Laws by Giles Jacob, 1721, p165 and Trial of Thomas Gordon, 5 July 1732 respectively)
From buggery we get the presumably derogatory term buggeranto. (for an example see The London Spy, part III, published 1703)
Molly
The preferred term used by the community was molly. Rictor Norton explains in Mother Clap’s Molly House:
The early church fathers stigmatised homosexuals as molls or sissies, and secular society called effeminate men molly-coddles and homosexuals mollies; having no other self-referring terms except the even less appealing Sodomite or Bugger, gay men transformed Molly into a term of positive self-identification, in exactly the same way that the modern subculture has transformed Gay (which derived originally from ‘gay girl’, meaning a female prostitute) into a term of pride and self-liberation.
Molly (plural mollies) was a noun:
Sukey Haws, being one Day in a pleasant Humour, inform’d Dalton of a Wedding (as they call it) some Time since, between Moll Irons, and another Molly,
~ James Dalton’s Narrative (1728)
Molly/mollied/mollying could also be a verb:
I was going down Fleet-Street, I was just come out of Jail. This Man, the Prosecutor, is as great a Villain as ever appear'd in the World. I was coming down Fleet-Street, so Molly says he; I said, I never mollied you. My Lord, I never laid my Hand upon him, nor touch'd him; I never touch'd the Man in my Life.
~ Trial of Richard Manning, (17 January 1746)
And mollying could be used as an adjective:
But they look'd a skew upon Mark Partridge, and call'd him a treacherous, blowing-up Mollying Bitch, and threatned that they'd Massacre any body that betray'd them.
~ Trial of Thomas Wright, (20 April 1726)
A molly house was house or tavern that catered to mollies. Molly houses would typically serve alcohol and often had music and dancing. Usually there was a room where mollies could have sex known as the chapel. (see Trial of Gabriel Lawrence, 20 April 1726 for an example of the term molly house in use, Trial of George Whytle, 20 April 1726 and Trial of Margaret Clap, 11 July 1726 for details on the chapel, and Trial of William Griffin, 20 April 1726 for molly houses taking lodgers.)
Mollies also had their own slang which I have a separate post on if you want to learn more about that.
Euphemisms
Euphemisms for men who had sex with other men included Back Gammon Player and Usher, or Gentleman of the Back Door. To navigate the windward passage was a euphemism for anal sex. (see The Classical Dictionary of the Vulgar Tongue, 1785.)
References to the classics were also sometimes used as euphemisms. A common example is Zeus's male lover Ganymede. (for an example see Public Advertiser, 4 Sept 1781)
Anal Sex Roles
The roles in anal sex were known as pathic (sometimes spelt Pathick) or patient (bottom) and agent (top). I have a longer post about the cultural perception of roles in anal sex if you're interested in that sort of thing.
Other Terms for Men Who Had Sex With Men
Pederast: In the 18th century the word pederasty was used synonymously with sodomy and did not denote age simply sex. An Universal Etymological English Dictionary (1726) defines “A pederast” as “a Buggerer” and “Pederasty” as “Buggery”.
Catamite: In particular catamite often, but not always, denoted the younger partner in a male-male sexual relationship. It was sometimes used to specifically describe boys but it was sometimes used it to describe men. Cocker's English Dictionary (1704) defines catamite as "a boy hired to be used contrary to nature, for Sodomy" but The New Royal and Universal English Dictionary (1763) defines catamite simply as "a sodomite." Catamite was also sometimes used as synonym for pathic.
Gomorrean: Like sodomite this one comes from the biblical story of Sodom and Gomorrah. However it wasn't nearly as commonly used. (for an example see The London Chronicle, 4 - 6 Jan 1757)
Madge Cull: This one came about towards the end of the century. It comes from a combination of Madge a slang term for “the female genitals” and Cull slang for “a man, a fellow, a chap.” (see Green’s Dictionary of Slang)
Women Who Had Sex With Women
Sodomy
While English common law did not consider sex between women sodomy this was not true across Europe. (see Louis Crompton, The Myth of Lesbian Impunity Capital Laws from 1270 to 1791) Most English colonies followed English common law however this aspect of the law was not unanimously agreed upon.
In 1636 Rev. John Cotton proposed to the General Court of Massachusetts a body of laws that would define sodomy as "a carnal fellowship of man with man, or woman with woman". (Crompton, p19)
In a 1779 bill submitted to the Virginia Assembly on crime and punishment Thomas Jefferson explicitly includes sex between women. He quotes Henry Finch's Law, or, a Discourse Thereof; in Four Books which defines sodomy as "carnal copulation against nature, to wit, of man or woman in the same sex, or of either of them with beasts." Jefferson disagrees with Finch on including bestiality because it "can never make any progress" and "cannot therefore be injurious to society in any great degree". However he doesn't dispute the inclusion of sex between women. He proposes that the punishment for sodomy be "if a man, by castration, if a woman, by cutting thro’ the cartilage of her nose a hole of one half inch diameter at the least." (see A Bill for Proportioning Crimes and Punishments in Cases Heretofore Capital, 18 June 1779)
While there was some disagreement on the legal definition of sodomy, colloquially if someone was talking about sodomy they were probably talking about sex between men. A clarification would likely be added if they were talking about women e.g. female sodomite.
Tribade
Coming from French tribade was defined in The New Pocket Dictionary of the French and English Languages (1781) as a "female sodomite". Tribade was used in English at least as early as 1585. It originally comes from the ancient Greek word τρίβειν meaning "rub" and is a reference to tribadism. The word tribadism however did not come into use until the 19th century. (see OED)
Sappho was a famous Tribade; as appears by the Testimonies of all the old Poets, but particularly from that beautiful Ode (addressed to one of the Ladies, with whom she was in Love) which Longinus has preserved, and which has ever been so highly esteemed by all the Critics.
~ William King, The Toast (1732)
Sapphic
Sapphic (sometimes spelt sapphick) originally meant "relating to, characteristic of, or reminiscent of Sappho or her writings". (OED) It became a term for sexual activity and sexual desire between women in reference of course to the accent Greek poet Sappho's love poems addressed to women. In fact in 18th century England Sappho was often cited as being the first woman who had ever had sex with another women.
Sappho, as she was one of the wittiest Women that ever the World bred, so she though with Reason, it would be expected she should make some Additions to a Science in which Womankind had been so successful: What dose she do then? Not content with our Sex, begins Amours with her own, and teaches the Female World a new Sort of Sin, call’d the Flats, that was follow’d not only in Lucian’s Time, but is practis’d frequently in Turkey, as well as at Twickenham at this day.
~ Satan’s Harvest Home (1749)
Sapphic is an adjective:
Look on that mountain of delight, Where grace and beauty doth unite, Where wreathed smiles must thrive; While Strawberry-hill at once doth prove, Taste, elegance, and Sapphick love, In gentle Kitty *****.
~ A Sapphick Epistle (1778)
Sapphism is a noun for the act or desire:
it has a Greek name now & is call’d Sapphism, but I never did hear of it in Italy where the Ladies are today exactly what Juvenal described them in his Time – neither better nor worse as I can find. Mrs Siddons has told me that her Sister was in personal Danger once from a female Fiend of this Sort; & I have no Reason to disbelieve the Assertion. Bath is a Cage of these unclean Birds I have a Notion, and London is a Sink for every Sin.
~ Hester Thrale Piozzi, Thraliana, 9 Dec 1795
Sapphist is a noun for the person:
Nature does get strangely out of Fashion sure enough: One hears of Things now, fit for the Pens of Petronius only, or Juvenal to record and satyrize: The Queen of France is at the Head of a Set of Monsters call’d by each other Sapphists, who boast her Example; and deserve to be thrown with the He Demons that haunt each other likewise, into Mount Vesuvius.
~ Hester Thrale Piozzi, Thraliana, 1 April 1789
Lesbian
Originally meaning "a native or inhabitant of the Greek island of Lesbos" (OED) this is another reference to Sappho who was from Lesbos.
However, this little Woman gave Myra more Pleasure than all the rest of her Lovers and Mistresses. She was therefore dignified with the Title of Chief of the Tribades or Lesbians.
~ William King, The Toast (1732)
Tommy
Tommy (plural tommies) is a fairly uniquely 18th century term as it doesn't seen to have been used earlier and is rarely used later. Speculatively it may be etymologically linked to tomboy which dates back to 1656. (OED)
Women and Men, in these unnat'ral Times, Are guilty equal of unnat'ral crimes: Woman with Woman act the Many Part, And kiss and press each other to the heart. Unnat'ral Crimes like these my Satire vex; I know a thousand Tommies 'mongst the Sex: And if they don't relinquish such a Crime, I'll give their Names to be the scoff of Time.
~ The Adulteress (1773)
Euphemisms
The game of flats, game at flats or simply flats was a euphemism for sex between women. Rictor Norton explains it was “a reference to games with playing cards, called ‘flats’, and an allusion to the rubbing together of two ‘flat’ female pudenda.” (Mother Clap’s Molly House, p233)
I am credibly informed, in order to render the Scheme of Iniquity still more extensive amongst us, a new and most abominable Vice has got footing among the W—n of Q—–y, by some call’d the Game at Flats;
~ Satan’s Harvest Home (1749)
In a diary entry Hester Thrale Piozzi repots "’tis a Joke in London now to say such a one visits Mrs. Darner". This was in reference to the rumours of sapphism that surrounded the sculptor Anne Damer. Piozzi goes on to recored a poem concerning Anne Damer's relationship with actress Elizabeth Farren that was being passed around her social circle:
Her little Stock of private Fame Will fall a Wreck to public Clamour, If Farren herds with her whose Name Approaches very near to Damn her.
~ Hester Thrale Piozzi, Thraliana, 9 Dec 1795 (see ‘Random Shafts of Malice?': The Outings of Anne Damer by Emma Donoghue for more on the rumours surrounding Anne Damer)
Absence of Sexual Attraction
With 18th century sexuality labels being action based rather than attraction based we have no exact equivalent for the word asexual. Just as we have no exact equivalent for the word homosexual. There was of course words for people who had never had sex (virgin, maiden) and words for people who planned on never having sex (celibate).
However this doesn't mean 18th century people had no way of talking about a lack of sexual attraction. The Chevalière d'Eon in a letter to the Comte de Broglie talks of "the natural lack of passion in my temperament, which has prevented my engaging in amorous intrigues”. Her lack of sexual interest became part of her self-styling as La Pucelle de Tonnerre (The Maiden of Tonnerre) after Joan of Arc who was known a La Pucelle d'Orléans (The Maiden of Orleans). (see D’Eon to the Comte de Broglie, 7 May 1771. Translated by Alfred Rieu, D'Eon de Beaumont, His Life and Times, p141; also for examples of the English press calling her La Pucelle d'Orléans see the Public Advertiser, 4 May & 11 June 1792)
The Third Sex/Gender
In the 18th century intersex people were predominantly referred to as hermaphrodites (while it is now considered offensive I will use it in this post as I think there is educational value in understanding it's historical use). In The Mysteries of Conjugal Love Reveal'd Written in French Nicholas de Venette explains that intersex people were permitted to "chuse either of the two Sexes". However if they strayed from the chosen role of man or woman they could be "punished like a Sodomite". (p465)
In the 18th century the words sex and gender were used somewhat synonymously. The word hermaphrodite along with third sex and third gender were used to describe not only intersex people but also gender nonconforming endosex people. Your clothes, interests, speech patterns and the way you move were all considered part of your sex.
Consider The Fribbleriad by David Garrick. Garrick was an actor known for playing fops. In the poem he portrays his critics as a group of effeminate men who were angry at him for they way he mocked them in his work:
In forty-eight— I well remember— Twelve years or more— the month November— May we no more such misery know! Since Garrick made OUR SEX a shew; And gave us up to such rude laughter, That few, ‘twas said, could hold their water: For He, that play'r, so mock’d our motions, Our dress, amusements, fancies, notions, So lisp’d our words and minc’d our steps, He made us pass for demi-reps. Tho’ wisely then we laugh’d it off, We’ll now return his wicked scoff.
"OUR SEX" is understood to be the sex of effeminate men. A sex distinct from that of acceptable manhood or womanhood which is defined by their "dress, amusements, fancies, notions" as well as the way they "lisp'd" their words and "minc’d" their steps.
John Bennett in his popular conduct book Letters to a Young Lady on a Variety of Useful and Interesting Subjects advises young women against wearing riding habits warning that they would "wholly unsex her". The Guardian reports that some people had "not injudiciously stiled" the riding Habit "Hermaphroditical". And The Spectator complains about riding Habits calling them an "Amphibious Dress" and describing women who wear them as "Hermaphrodites" and a "Mixture of two Sexes in one Person". (The Guardian, 1 September 1713, reprinted in The Guardian edited by John Calhoun Stephens, p 486; The Spectator 19 July, 1712)
The word amphibious is one that comes up a lot in the 18th century in regards to gender. A dictionary of the English language (1794) defines amphibious as "living in two elements". John Bennett describes effeminate men as "poor amphibious animals, that the best naturalists know not under what class to arrange."
Alexander Pope famously called Lord Hervey an "Amphibious Thing!" that acts "either Part". Lady Mary Wortley Montagu said that "this world consisted of men, women, and Herveys". And William Pulteney describes him as "delicate Hermaphodite", "a pretty, little, Master-Miss" and "a Lady Himself; or at least such a nice Composition of the two Sexes, that it is difficult to distinguish which is most predominant." (Alexander Pope, Epistle to Dr Arbuthnot; The Letters and Works of Lady Mary Wortley Montagu edited by Lord Wharncliffe, v1, p95; William Pulteney, A Proper Reply To a late Scurrilous Libel)
Macaroni, amazon, virago, fop, petit-maitre, coxcomb, amphibious, unsex, dandy, namby-pamby, he-she things, lady-fellow, master-miss, fribble, dubious gender. These were all terms to describe gender nonconforming people. Many of these terms were used in a derogatory way but not all of them were intended as such and some GNC people identified with some of these terms. For example a young Charles James Fox described himself as a petit-maitre in his 18 Oct, 1763 letter to his father. While at Eton, which he found "more disagreeable than I imagined", he laments "you may see the petit maître de Paris is converted into an Oxford Pedant."
Many of the people who were labeled as third sex/gender would not necessarily have identified as such. With even the smallest deviation from the norm giving rise to the label. Including one 1737 article which claimed that "Ugly Women" may "more properly be call'd a Third Sex, than a Part of the Fair one". (Common Sense, or The Englishman's Journal, 28, Feb)
Gender Presentation Through Gendered Language
While there is no real equivalent for the word transgender in 18th century English this doesn't mean people had no way of expressing their gender though language. People referred to themselves as being men, women, both or neither. Gendered names, titles and pronouns were also used to express one's gender.
The Chevalière d'Eon
D'Eon asserted her gender identity though gendered names, pronouns and titles. When she started openly living as a women she changed her first name to Charlotte making her full name Charlotte-Geneviève-Louise-Auguste-André-Timothée d’Eon de Beaumont. However she preferred the name Geneviève and would often write her name simply Geneviève d'Eon.

[Admission-ticket for Geneviéve d'Eon, with red seal; c.1793; via The British Museum (C,2.3)]
D'Eon used she/her pronouns. Here is an example of her using she/her pronouns for herself when writing in third person:

[Invitation from the Chevalière d’Eon to Lord Besborough; c.1791; via The British Museum (D,1.268-272)]
As she was French d'Eon used French titles even in English. She would sometimes use the title Mademoiselle (a title for unmarried women) but other times she used Chevalière. In 1763 she was awarded the Cross of Saint-Louis and with that came the masculine title Chevalier. When she started openly living as a women she switched from the masculine Chevalier to the feminine Chevalière. Perhaps the most fun example of her using the feminine Chevalière is the sword she gifted to George Keate which was inscribed: "Donné par la Chevalïere d’Eon à son ancïen Amï Geo: Keate Esquïre. 1777"


[The Chevalière d’Eon’s Sword, hilt: c.1700s, blade: c.mid-1600s, inscription: c.1777, photos via the Royal Armouries Museum (IX.2034A)]
Public Universal Friend
The Public Universal Friend claimed to be a genderless spirit sent by god resurrected in the body of Jemima Wilkinson after she had succumbed to a fever in 1776. The Public Universal Friend gained a small but devoted group of followers that understood and respected the Friend as a genderless being. When one traveler asked for directions to "Jemima Wilkinson's house" a women replied that "she knew no such person; "the friend" lived a little piece below." (A Ride to Niagara in 1809 by Cooper Thomas, p37)
For the most part followers of the Public Universal Friend avoided using gendered pronouns for the Friend*. However they did not use gender neutral pronouns (such as they/them) but instead avoided third person pronouns completely. You can see an example of the sort of gender neutral language used for the friend in this letter from Sarah Richards to Ruth Pritchard:
Dear Ruth This is to be a Messenger of my Love to thee. Hold out faith and patience. Thy letter was very welcome to me. I want Thee should make ready to come where the Friend is in this Town. The Friend has got land enough here for all that will be faithful & true. Dear Ruth, I will inform thee that Benedict has given the Friend a Deed of some land in the second Seventh in the Boston perhemption, which Deed contains five lotts and the Friend has made use of my name to hold it in trust for the Friend, and now I hope the Friends will have a home, and like wise for the poor friends and such as have no helper, here no intruding feet cant enter. Farewell form thy Affectionate Friend, Sarah Richards
~ Sarah Richards to Ruth Pritchard, March 1793 (printed in The Unquiet World by Frances Dumas, p166)
* In contrast to followers that avoided gendered pronouns completely ex-follower Abner Brownell claimed that some followers called the Friend "him." (see A Mighty Baptism edited by Susan Juster & Lisa MacFarlane, p28)
It's impossible to seperate the Friend's genderlessness from the claim that the Friend was a messenger sent by god resurrected in the body of Jemima Wilkinson. The followers of the Public Universal Friend used genderless language as a way to indicate their religious devotion. In "Indescribable Being" Theological Performances of Genderlessness in the Society of the Publick Universal Friend, 1776-1819 Scott Larson explains:
The language one chose to describe the Friend indicated whether one was part of the community of the saved or part of the "wicked world." Conversely, community members and followers used the name "the Friend" quite deliberately, and that use became a marker of belonging. This sense of belonging could last longer than the community itself did. Huldah Davis, who was a child when the Friend left time in 1819, shared her memories of the Friend in 1895. In her recollections, Davis refers to Jemima Wilkinson but is careful to note that her parents, followers of the Friend, always referred to "the Friend," and Davis uses the community's language through most of her account. Language choices could also mark points of entering and exiting the community, as the apostate and denouncer Abner Brownell refers to "The Friend" in diary entries written during the time of his membership in the Friend's community but then calls "her" "Jemima Wilkinson" in his later published denunciation, Enthusiastical Errors, Described and Decried.
Mollies and Maiden Names
Gendered language could be used to express queer identity without necessarily expressing a transgender identity. Mollies took on feminine sobriquets known as maiden names. A maiden name was a typically made up of a combination of either a feminine title or name (molly and variations being the most popular) and often a reference to something notable about the individual. It could be a reference to their profession for example Orange Mary was an orange merchant, Dip-Candle Mary was a tallow chandler and Old Fish Hannah a fisherman. It could be a reference to where they were from for example Mrs. Girl of Redriff was presumably from Redriff. Some maiden names were somewhat suggestive like Miss Sweet Lips or Molly Soft-buttocks.
(Sources for maiden names: Orange Mary, Dip-Candle Mary, Old Fish Hannah, and Mrs. Girl of Redriff are mentioned in James Dalton's Narrative; Miss Sweet Lips is mentioned in The Phoenix of Sodom by Robert Holloway; Molly Soft-buttocks is mentioned in Account of the Life and Actions of Joseph Powis)
While mollies took on these feminine names, they more often than not still lived as men. Most mollies wore men's clothes, used he/him pronouns and referred to their partners as their husbands not their wives. (for the use of husband in the molly subculture see the trial of Martin Mackintosh, 11 July 1726 and the trial of George Whytle, 20 April 1726)
However some mollies did wear women's clothes and used (at least some of the time) feminine pronouns. Take for example Princess Seraphina who during the trial of Thomas Gordon (5 July 1732) is described by Mary Poplet as follows:
I have known her Highness a pretty while, she us’d to come to my House from Mr. Tull, to enquire after some Gentlemen of no very good Character; I have seen her several times in Women’s Cloaths, she commonly us’d to wear a white Gown, and a scarlet Cloak, with her Hair frizzled and curl’d all round her Forehead; and then she would so flutter her Fan, and make such fine Curties, that you would not have known her from a Woman: She takes great Delight in Balls and Masquerades, and always chuses to appear at them in a Female Dress, that she may have the Satisfaction of dancing with fine Gentlemen. Her Highness lives with Mr. Tull in Eagle-Court in the Strand, and calls him her Master, because she was Nurse to him and his Wife when they were both in a Salivation; but the Princess is rather Mr. Tull’s Friend, than his domestick Servant. I never heard that she had any other Name than the Princess Sraphina.
On a final note I would also recommend looking up many of these terms in the Oxford English Dictionary (you might be able to access this for free through your library) and Green's Dictionary of Slang both of which include multiple examples in use.
#sorry this took so long I couldn't resist making it far too long#if you want me to talk your ear off just ask me about 18th century queer language its my favourite topic#queer history
149 notes
·
View notes
Text
Re: Dandyism
The inherent problem with the “foncy poncy oppressive English narrative” that is definitely historical revisionism.
1) anyone who was anyone in the 18th century (Hamilton, Tallmadge, Major André, Washington’s other aides to camp and the British generals) would’ve both presented as a “dandy” it was a symbol of status and being cultured and/or well read.
2) imperialism cuts both ways and both sides brutalized and lied to black and indigenous folks. Don’t get me, a brown person, started on the British Raj. (Reading 1) (reading 2)
youtube
youtube
youtube
youtube
Prompted by this post also I highly recommend The Vampire Lestat, Tallmadge’s memoir, the scarlet pimpernel, and dangerous liaisons.
#meerathehistorian#dandy#dandyism#quaintrelle#quaintrelleism#history#long post tw#fashion history#18th century#queer history#18th century history#european history#american history#english history#history of fashion#bisexual#lgbtq+#queer#american revolution#alexander hamilton#ben tallmadge#benjamin tallmadge#lord byron#regency#historical fashion#historical references#turn washington's spies#turn: washington's spies#amc turn#turn amc
200 notes
·
View notes
Text


jan and nace in late 1700s outfits (nace's vest has florals :))
but i know know my target audience, so here:


late 1700s jan playing a lute and a baroque guitar
#my justification for why he is playing baroque instruments is that we know jan likes vintage guitars#THEREFORE late 1700s jan would be into early 1700s instruments yesyes you see the vision???#on the other hand historical accuracy was thrown out of the window a long time ago with this “series”#old timey joker out#jan peteh#nace jordan#doodle type thing#joker out#joker out fanart#fanart#my art#traditional art#artists on tumblr#18th century
130 notes
·
View notes
Text



#rococo#historical fashion#fashion#historical#history#historical clothing#historical dress#long dress#textiles#dress#ball gown#gown#high fashion#fahsion#18th century fashion#old fashioned#1700s fashion#1700s#18th century#artwork#etsyshop
502 notes
·
View notes
Text
a lot of people, when they start learning how to sew, will see instructions about pressing carefully and staystitching and basting and grainline and machine tension and such, and will go "ehh, I can ignore that and save some time" and then later they'll go "why do my seams look so bad? :(" and. well.. that's why.
#and that was me to some degree for a good long while#mainly with basting. god I hated basting for so so long#but now it's my beloved way to the nicest neatest flat felled seams. basting is good!#I also stubbornly refused to learn to use a thimble until I was forced to for work#and it turns out thimbles are great!#sewing#I never skimped out on ironing at least! you NEED to press your seams dammit!#I also don't usually do staytstitching because it's not necessary on my 18th century tailored & square cut things#but for stuff like rayon summer nightgowns with curved necklines and armholes? IMPERATIVE!
1K notes
·
View notes
Text

Miniature of Archduchesses Maria Josepha and Maria Johanna Gabriela of Austria, with a jewelry box.
#maria josepha of austria#Maria Johanna Gabriela of Austria#archduchess#austria#house of habsburg lorraine#18th century#long live the queue
45 notes
·
View notes