#India’s defence technology
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Advancing India Defence Technology Insights by Delhi Policy Group
Delhi Policy Group delves into the evolution of India’s defence technology , highlighting its strategic advancements and challenges. Through in-depth research, the organization examines India’s efforts in modernizing its defense capabilities, fostering self-reliance, and enhancing global partnerships. Addressing key areas like missile systems .
0 notes
Text
youtube
#Youtube#p8i Poseidon#p8 Poseidon#maritime patrol aircraft#aviation technology#aviation enthusiast#aviation#military technology#anti submarine weapon#india#indian navy#indian army#indian airforce#military#defense#defence#warfare
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
JSW Defence to invest $90 million to bring American Shield AI's fixed-wing drone to India
By N. C. Bipindra Mumbai: Indian firm JSW Defence Private Limited, part of the US$24-billion JSW Group, today announced a “strategic partnership” with Shield AI Inc., a leading American defence technology company, to indigenise and manufacture Shield AI’s ‘V-BAT‘ fixed-wing Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) in India. “This collaboration marks a significant step in boosting India’s defence…
#Aircraft#American#Armed Forces#Brandon Tseng#Defence#Defense#Group 3 UAS#Group 5 UAS#India#Indian#Indian Armed Forces#Industry#JSW Defence#JSW Defence Private Limited#JSW Group#Major Defence Partner#Major Defense Partner#Manufacturing#Marine Expeditionary Units#MEUs#Military#Parth Jindal#Partnership#Plane#Production#Shield AI#Stategic Authorization Tier 1#Technology#UAE#UAS
0 notes
Text
Zen Technologies Wins Major Defence Maintenance Contract
Zen Technologies bags major defence maintenance contract: New Delhi, India – Zen Technologies Limited, a leading Indian defense technology company, has secured a significant annual maintenance contract (AMC) valued at Rs 46 crore (approximately $5.5 million) with the India’s Ministry of Defence. The five-year contract will cover the upkeep and maintenance of various simulators designed and…
0 notes
Text
DRDO awards multiple contracts to Indian defence startups
DRDO awards 7 new projects to Indian startups: India’s Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has awarded seven new defence projects to private Indian companies, with a particular focus on nurturing micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) and startups. These projects have been awarded to Indian defence startups spread across the country, from Delhi-NCR to Maharashtra to…
#Accord Software & Systems Pvt Ltd#Alohatech Private Limited#Craftlogic Labs Pvt Ltd#Data Pattern India Limited#Defence Ministry#Defence Startups#DRDO#IROV Technologies Pvt Limited#Oxygen 2 Innovation Pvt Ltd#Sagar Defence Engineering#Technology Development Fund
0 notes
Text
CST India and IIT Jammu Announce Groundbreaking Collaboration
Building on their recent successful partnership, CST Advanced Systems and IIT Jammu are currently developing two ground-breaking initiatives that will benefit both the military and the commercial sector equally. These initiatives will be enhanced by CST India's competence in cybersecurity, defense and security systems integration, and IIT Jammu's esteemed research capabilities, which will guarantee the creation of cutting-edge, dependable, and secure solutions. These initiatives will have a significant positive impact on military operations as well as the ongoing effort to provide safe, dependable communication and navigation in challenging environments.

Read Full news: https://www.businesswireindia.com/cst-advanced-systems-and-iit-jammu-collaborate-to-revolutionize-future-warfare-90656.html
1 note
·
View note
Text
Space Technology Opportunity in India

Written By: Jagriti Shahi
Introduction:
Entrepreneurship in space technology in India has been gaining momentum in recent years. The Indian government has been actively promoting the development of the space sector, and private companies are playing an increasingly important role.
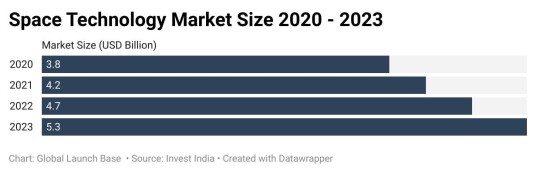
As the nation liberalizes its space sector, a diverse array of players are contributing to the burgeoning space ecosystem. Entrepreneurs are venturing into satellite manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of launch services, delving into space exploration, and exploring innovative solutions for satellite-based communication. The landscape is further enriched by collaborative efforts between private entities, government agencies, and academic institutions, fostering a dynamic environment for research and development.
In this context, it's crucial to explore the challenges and opportunities that define the entrepreneurial spirit in India's space technology sector. Regulatory hurdles, infrastructure development, and the need for sustained investments are among the challenges that entrepreneurs face. However, with increasing investor interest, a robust policy framework, and a commitment to fostering innovation, India's entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are poised to shape the nation's narrative in the cosmic domain. This dynamic interplay of public and private entities is not only propelling India's space capabilities but is also contributing to the global discourse on the commercialization and exploration of space.
Here are some key aspects of entrepreneurship in space technology in India:
Government Initiatives:New Space Policy: The Indian government has introduced policies to encourage private sector participation in space activities. The New Space India Limited (NSIL) was established to promote, commercially exploit, and transfer technologies developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).Liberalization: The government has liberalized the space sector, allowing private companies to undertake a wide range of space-related activities, including satellite launches, space exploration, and satellite communication services. (ISRO) Initiatives: Antrix Corporation: Antrix is the commercial arm of ISRO, and it collaborates with private players for the commercialization of space-related products and services.: SEED is a program initiated by ISRO to promote startups in the space sector by providing them with opportunities for collaboration and technology transfer.: NSIL is a central public sector enterprise (CPSE) under the Department of Space. It plays a crucial role in commercializing space products, technical consultancy services, and transfer of technologies.: ISRO has been actively engaging with startups, providing them access to its facilities, expertise, and technology.: The Department of Space in India oversees the country's space program. It may introduce schemes and programs to support space technology startups and entrepreneurs. (AIM): AIM, a flagship initiative of the NITI Aayog, supports innovation and entrepreneurship in various sectors. It may have programs and funding opportunities that space technology startups can explore. (NIF): NIF supports grassroots innovations and may provide support to startups working on innovative space technologies.
Private Space Companies:Startups: Several startups in India are focusing on various aspects of space technology. Some are involved in satellite manufacturing, launch services, data analytics from space, and more.Launch Services: Companies like Agnikul Cosmos, Skyroot Aerospace, and Pixxel are working on developing small satellite launch vehicles to provide cost-effective and flexible launch options.
Space Exploration and Research: Interplanetary Missions: ISRO has been actively involved in space exploration, and private companies are expressing interest in participating in future interplanetary missions.Research and Development: Private entities are engaging in research and development activities, contributing to advancements in satellite technology, propulsion systems, and other space-related technologies.
Satellite Manufacturing:Private Satellite Manufacturers: Companies like Exseed Space and Bellatrix Aerospace are involved in the manufacturing of satellites, catering to various purposes such as communication, Earth observation, and scientific research.
Communication Services:Telecommunication Satellites: Private companies are exploring opportunities to provide satellite-based communication services. This includes both broadband internet services and other communication solutions.
Funding and Investments:Investor Interest: The space technology sector in India has attracted attention from investors. Funding rounds for space startups have been on the rise, indicating confidence in the potential growth of the industry.
Collaborations and Partnerships:
Industry-Academia Collaboration: Partnerships between private companies, government organizations, and academic institutions are fostering innovation and research in the space sector.
The Indian space technology ecosystem is evolving, and with continued government support, entrepreneurial ventures in space technology are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of the Indian space industry.
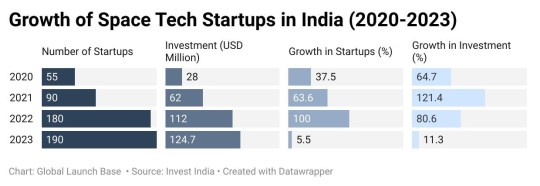
The number of space tech startups in India has witnessed explosive growth, increasing by almost five times in just five years. Investments in the sector have also seen a sharp rise, from $17 million in 2019 to an estimated $124.7 million in 2023.
Commercialization of Space Activities: With India's proven track record in satellite launches and space technology, there is a substantial potential for the commercialization of space activities. The burgeoning demand for satellite-based services, including communication, arth observation, and navigation, opens up opportunities for private entities to actively participate in the space industry. As the cost of space access continues to decrease, private companies can explore ventures such as satellite manufacturing, space tourism, and satellite-based applications, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
International Collaborations: Collaborations with other space-faring nations present a promising avenue for India to augment its space capabilities. Joint ventures, knowledge exchange, and technology transfer can accelerate innovation and enhance the efficiency of space missions. ISRO has already established itself as a reliable partner for international launches, and expanding collaborative efforts can lead to shared resources, reduced costs, and a more diversified approach to space exploration. As India continues to engage in global partnerships, it can leverage collective expertise for ambitious endeavors beyond Earth's orbit.
Innovation in Space Technology: Investments in research and development (R&D) can catapult India into the forefront of space innovation. Emphasis on cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, advanced materials, and propulsion systems can revolutionize space missions. The development of reusable launch vehicles, like the ongoing efforts in creating a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), can significantly reduce launch costs, making space exploration more sustainable. Encouraging a culture of innovation, fostering collaboration between academia and industry, and providing incentives for R&D initiatives can fuel breakthroughs in space technology.
Space Applications for Sustainable Development: Leveraging space technology for sustainable development on Earth is an untapped frontier. Utilizing satellite data for precision agriculture, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and resource mapping can contribute to addressing pressing global challenges. By integrating space-based solutions into sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and urban planning, India can harness the power of space technology for inclusive and sustainable development, bringing tangible benefits to its citizens and contributing to global initiatives.
Expansion of Interplanetary Exploration: Building on the success of Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), India has the potential to expand its interplanetary exploration efforts. Initiatives for exploring other celestial bodies, such as Venus or asteroids, can contribute to humanity's understanding of the solar system and beyond. A strategic focus on ambitious interplanetary missions can position India as a key player in the broader scientific community and foster international collaboration in the exploration of the cosmos.
Trending Technologies in India's Space Industry:
Nanotechnology: The integration of nanotechnology in space technology has the potential to revolutionize spacecraft design, materials, and instrumentation. Nanosatellites, with their miniaturized components, are becoming increasingly popular for cost-effective and innovative space missions. India can leverage nanotechnology for lightweight yet robust spacecraft, enhancing mission efficiency and scientific capabilities.
Companies: Nano-Tech SpA, Kalva Nanotech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are playing a pivotal role in data analysis, image processing, and autonomous decision-making in space missions. India can explore AI applications for real-time data interpretation, automated navigation, and predictive maintenance of spacecraft. Incorporating machine learning algorithms into Earth observation data analysis can significantly enhance the understanding of environmental changes.
Companies: Aadyah Aerospace, Blue Sky Analytics
Quantum Computing: Quantum computing holds the promise of solving complex computational problems beyond the capabilities of classical computers. In the space sector, quantum computing can be utilized for optimizing mission trajectories, simulating quantum systems, and enhancing the security of communication channels. India's focus on quantum computing research can contribute to advancements in space-related computations.
Companies: QpiAI, BosonQ
3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: The adoption of 3D printing in space technology can revolutionize the manufacturing process, enabling the production of complex and lightweight structures. India can benefit from 3D printing for rapid prototyping, cost-effective manufacturing of satellite components, and even on-demand production during long-duration space missions.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos, EOS India
Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers secure and transparent data management, making it applicable to space-based applications such as satellite communication, data storage, and secure information sharing. By incorporating blockchain, India can enhance the security and integrity of space-related data and transactions.
Companies: SpaceTime Labs, Aryaka Networks
Solar Sail Technology: Solar sails, propelled by the pressure of sunlight, offer a sustainable and efficient means of propulsion for spacecraft. This technology can be harnessed for deep-space exploration, enabling missions to travel vast distances with minimal fuel requirements. India's exploration programs can benefit from research and development in solar sail technology for extended-duration missions.
Companies: Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology (IIST), IIT Bombay - Aerospace Engineering Department
Hyperspectral Imaging: Hyperspectral imaging involves capturing a wide range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. This technology is instrumental in Earth observation, resource mapping, and environmental monitoring. India can explore the integration of hyperspectral imaging in its satellite payloads for enhanced remote sensing capabilities.
Companies: Pixxel, Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd
Internet of Things (IoT) for Space: The application of IoT in space technology involves connecting devices and sensors on satellites and spacecraft to gather and transmit data. This interconnected network can facilitate efficient communication, data collection, and collaborative decision-making during space missions. India can explore IoT applications for enhanced space situational awareness and mission coordination.
Companies: Agnikul Cosmos
As India looks to the future, embracing these trending technologies will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in space exploration and satellite technology. By actively incorporating these innovations into its space programs, India can not only enhance mission success but also contribute to the global advancement of space technology. Collaborations with research institutions, startups, and the private sector will play a vital role in driving these technological advancements in India's space industry.
Challenges and the Way Forward:
Despite its successes, India's space program faces challenges such as increased competition, budget constraints, and the need for continuous innovation. To overcome these challenges, sustained government support, collaboration with private entities, and a focus on skill development in the space sector are crucial.
Increased Global Competition: The space industry is becoming increasingly competitive with the emergence of new players and the commercialization of space activities. To stay ahead, India must continuously innovate, streamline its processes, and invest in cutting-edge technologies. Developing a robust ecosystem for space startups and fostering public-private partnerships can enhance India's competitiveness in the global space market.
Budget Constraints: Despite commendable achievements, budget constraints pose a challenge for sustaining and expanding India's space endeavors. A consistent and increased allocation of funds to ISRO, along with exploring innovative funding mechanisms, will be crucial. Engaging with the private sector for joint ventures and commercial space activities can help alleviate financial constraints and promote economic sustainability in the long run.
Human Resource Development: The growth of India's space program necessitates a skilled workforce capable of handling complex missions. Investing in education and training programs in collaboration with academic institutions can ensure a steady supply of skilled professionals in fields such as aerospace engineering, astrophysics, and data sciences. This will not only address the current workforce requirements but also fuel future innovations in space technology.
Technological Advancements: Rapid technological advancements globally require India to stay at the forefront of innovation. Embracing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and advanced propulsion systems will be essential. Establishing research and development centers dedicated to space technology innovation can facilitate the integration of these advancements into future missions.
Space Debris Management: The increasing number of satellites and space missions contribute to the growing issue of space debris. India needs to actively participate in international efforts to address space debris management, adopting sustainable practices in satellite design and end-of-life disposal. Research into debris removal technologies and international collaboration on space traffic management will be pivotal in ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities.
Climate Change Monitoring: With the rising global concerns about climate change, space technology plays a crucial role in monitoring environmental indicators. India can take a leadership role in developing satellite-based solutions for climate monitoring, disaster response, and sustainable resource management. This requires a dedicated focus on Earth observation satellites, advanced sensors, and data analytics.
Enhanced Space Diplomacy: Strengthening space diplomacy is essential for India to expand its global influence in the space arena. Engaging in collaborative space missions, sharing scientific knowledge, and participating in international forums will enhance India's standing as a responsible space-faring nation. Forming strategic partnerships with countries interested in space exploration can open up new avenues for cooperation and joint missions.
Conclusion:
India's journey in space technology has been nothing short of remarkable, with ISRO consistently pushing the boundaries of innovation. As the nation continues to invest in space exploration, the opportunities for growth, collaboration, and technological advancements are boundless. The future holds exciting possibilities for India's space technology sector, positioning the country as a key player in the global space community.
About Global Launch Base:
Global Launch Base helps international startups expand in India. Our services include market research, validation through surveys, developing a network, building partnerships, fundraising, and strategy revenue growth. Get in touch to learn more about us.
Contact Info:
Website: www.globallaunchbase.com
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/globallaunchbase/
Email: [email protected]
#ISRO - Indian Space Research Organization#NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)#SEED(Social Entrepreneurship Empowerment Development)#Atal Innovation Mission Official#National Innovation Foundation - India#Nano-Tech SpA#Kalva Nanotech#AADYAH Aerospace Private Limited#Blue Sky Analytics#QpiAI#BosonQ Psi (BQP)#AgniKul Cosmos#EOS#Spacetime Labs#Aryaka#Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology#Aerospace Engineering Association IIT Bombay#Pixxel#Paras Defence & Space Technologies Ltd.#AgniKul Cosmos hashtag#SpaceTechnologyInIndia hashtag#IndianSpaceProgram hashtag#ISROOpportunities hashtag#SpaceIndustryGrowthIndia hashtag#SpaceResearchOrganizationsIndia hashtag#SatelliteTechnologyOpportunities hashtag#IndianSpaceExploration hashtag#ISROAchievements hashtag#SpaceScienceCareersIndia hashtag#SpaceTechnologyTrends hashtag
0 notes
Text
What Happened to the S-500? Why do We Never See This System in Action? - Technology Org
New Post has been published on https://thedigitalinsider.com/what-happened-to-the-s-500-why-do-we-never-see-this-system-in-action-technology-org/
What Happened to the S-500? Why do We Never See This System in Action? - Technology Org
If you followed Russian media, you would quickly notice a strong belief in superior weapons coming. The Sarmat missile does seem impressive, but is it really a complete game-changer? What is happening with the T14 Armata main battle tank? And what in the world happened to the S-500 missile system? Is it really operational or is it just another Armata story?
S-500 air-defence system launcher. This system can allegedly take down intercontinental ballistic missiles. Image credit: Пресс-служба Минобороны РФ via Wikimedia (CC BY 4.0)
Russians rely on the S-400 systems for their air defense. The S-300, which is a bit older, is used as well, including against ground targets. However, we never even hear about the S-500 Triumfator-M anymore. This system was not designed to replace the S-400 – both of these air defense systems were meant to work in parallel.
The S-500 is way more advanced and is armed with hypersonic missiles – the S-400 missiles are slower. The S-500 is meant to attack all kinds of targets, including intercontinental ballistic missiles and hypersonic cruise missiles.
Initially, it was planned that the S-500 would become operational in 2014, but that didn’t happen. This was a huge hit to the Russian military industry, because India and Turkey were looking into potentially becoming foreign buyers of the S-500.
The system, reportedly, became operational in 2021 and is currently in service, but there is no way of knowing that. Also, Russia probably has just a handful of them and with the war in Ukraine boiling the development and production of the S-500 is probably very slow or entirely halted. Even when talking about the latest Russian achievements in missile technology Russia’s defence minister Sergey Shoigu pretty much skips the S-500.
The Defense News reports that missile manufacturer Almaz-Antey has increased production recently, but is making more practical weapons that are being actively used in the war in Ukraine, not some fantasy project S-500. The S-500 is simply drowning in problems.
Back in 2020, the cost for one S-500 system was believed to be around $700-$800 million dollars, but this estimate increased to $2.5 billion in 2023. This is a huge cost for something that has such dubious usefulness. Can it actually target intercontinental ballistic missiles?
Russia has no way of testing that. The system itself is one thing, but what about the consumables – can Russia make the missiles? It’s been reported that the S-500 will use missiles that have 600 km range. However, making them is incredibly difficult now that Russia has no way to reach modern electronics.
And so the S-500 is falling out of the area of conversation. In August Shoigu was talking about the missiles Russia is making, but didn’t even mention the S-500. It is very likely that there is just one S-500 in existence and it might not even be fully operational.
Written by Povilas M.
Sources: Focus.ua, Wikipedia
#2023#air#air defence#air defense#Authored post#ballistic missiles#billion#boiling#defense#development#Electronics#Featured Military news#game#India#Industry#it#media#military#military industry#Military technology#missiles#News#One#Production#project#russia#Russia Ukraine War#Special post#Spotlight news#StandWithUkraine
0 notes
Link
Held yesterday in Delhi, the 2 plus 2 dialogue, serves as a means to discuss and evaluate all dimensions of the India-UK Comprehensive Strategic Partnership.
#India UK 2+2#british ministry of defence#trade#energy#health#civil aviation#technologies#mea india#ministry of external affairs india#maritime security#international cooperation#comprehensive strategic partnership#India UK 2 Plus 2#humanitarian assistance#Foreign and Defence Dialogue#defence dialogue#India UK Dialogue#hadr#fcdo#counter terrorism#news#news update#news blog#blogging
0 notes
Text
Difference Between Ballistic And Cruise Missile

0 notes
Text
The grenade
The grenade (grenade is likely derived from the French word spelled exactly the same, meaning pomegranate, as the bomb is reminiscent of the many-seeded fruit in size and shape. Its first use in English dates from the 1590s.) as we know it today is not a modern invention - on the contrary, it has its origins in late antiquity and the early Middle Ages.
First grenades appeared in the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire not long after the reign of Leo III (717-741). Byzantine soldiers learnt that Greek fire (a mixture of sulphur and oil), a Byzantine invention from the previous century, could be thrown at the enemy not only with flamethrowers but also in stone and ceramic vessels.

Byzantine " Greek Fire" Grenade, c. 800-1000 AD
With the invention of gunpowder in Song China (960-1279), weapons known as ‘thunderbolts’ were created by soldiers packing gunpowder into ceramic or metal vessels with fuses. In a military book from the year 1044, the Wujing Zongyao (Collection of Military Classics), various gunpowder recipes are described in which, according to Joseph Needham, the prototype of the modern hand grenade can be found.
The grenades (pào) are made of cast iron, are the size of a bowl and have the shape of a ball. They contain half a pound of ‘divine fire’ (shén huǒ, gunpowder) inside. They are sent by an eruptor (mu pào) towards the enemy camp, and when they arrive there, a sound like a thunderclap is heard and flashes of light appear. If ten of these grenades are successfully fired at the enemy camp, the whole place goes up in flames.
Grenade-like devices were also known in ancient India. In a Persian historical account from the 12th century, the Mojmal al-Tawarikh, a terracotta elephant filled with explosives was hidden in a chariot with a fuse and exploded as the invading army approached.
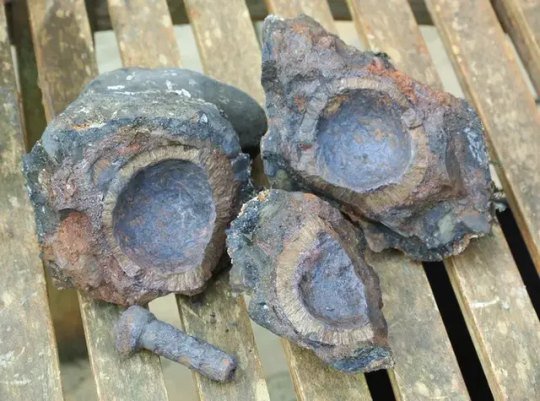

These encrusted hand grenades were washed up from a 17th-century pirate shipwreck, Dollar Cove, in the coastal Gunwalloe district of Cornwall's Lizard Peninsula
The first cast-iron bombs and shells appeared in Europe in 1467, where they were initially used in the siege and defence of castles and fortresses. In the mid-17th century, infantrymen known as ‘grenadiers’ emerged in European armies, specialising in shock and close combat, usually using grenades and engaging in fierce hand-to-hand combat. But grenades have also been in use at sea since the 17th century. They were used to inflict as much personal damage as possible below deck after boarding a ship by throwing the grenades underneath.
After the middle of the 19th century, grenades were used extensively in the Crimean War and the American Civil War. Before they changed in design and function to be used in the trenches, especially in the First World War and later. They are still in use today.
Forbes, Robert James (1993). Studies in Ancient Technology
Thomas Enke: Grundlagen der Waffen- und Munitionstechnik
David Harding (Hrsg.): Waffen-Enzyklopädie
Bertram Kropak: Die geschichtliche Entwicklung der Handgranaten. In: DWJ Deutsches Waffen Journal. 1970
#naval artifacts#naval weapons#grenade#ancient seafaring#medieval seafaring#age of sail#age of steam#today#naval history
124 notes
·
View notes
Text
Understanding the Indo-Pacific Strategy with Delhi Policy Group
Delhi Policy Group provides in-depth insights into the Indo Pacific strategy, analyzing its impact on regional stability and global politics. Our experts delve into the strategic interests and policies shaping this vital region, offering comprehensive reports and discussions. Stay informed about the geopolitical dynamics and economic initiatives influencing the Indo-Pacific.
0 notes
Text
Israel's willingness to share its technology provided the Indian military with a unique opportunity to reverse the disappointments of its arms industry that neither lived up to expectations nor delivered the "self-sufficiency" repeatedly promised and desired by the security establishment. Little wonder then that Richard Bitzinger described the Indo-Israeli arms trade relationship as "symbiotic." N.A.K. Browne agreed: "India's quest for technology and Israel's need for economizing defence research have therefore become complimentary [sic]."
By 2013, it wasn't especially clear how the relationship would proceed given the soft-pedalling of public engagements. PM Singh appeared to have avoided meeting or being seen with the Israeli government, particularly Netanyahu. But Singh's government had courted Zionist lobby groups in the U.S. in the lead up to the nuclear deal of 2005, and precipitated closer economic ties with Israel even as they mercilessly pounded Gaza in 2008/9 and in 2012. The rhetoric around India's commitment to Palestine remained the same. "We are deeply concerned at the steep escalation of violence between Israel and Palestine, focused around Gaza, that threatens the peace and security of that region," the Ministry of External Affairs said in November 2012, as Israel bombed Gaza beyond repair. In response to a question seeking clarity over India's relationship with Israel in parliament in December 2013, Edappakath Ahamed, India's Minister of State in the Ministry of External Affairs, replied: "India's relations with Israel stand on their own and are not at the expense of strong, time-tested and historic ties with the Arab world. Notwithstanding growing ties with Israel, there has been no change in the traditional policy of strong support to the Arab and the Palestinian cause."
Azad Essa, Hostile Homelands: The New Alliance Between India and Israel
9 notes
·
View notes
Text
Sweden’s Saab sets up Carl-Gustaf factory in India under first-ever 100% FDI
By N. C. Bipindra New Delhi: Sweden’s Saab announced today that it is setting up a production facility in India for its legendary Carl-Gustaf’s latest weapon system through the 100 percent Foreign Direct Investment route. The Swedish defence firm’s senior officials said they were hopeful of meeting the entire need of Indian armed forces for the M4 variant of the Carl-Gustaf and export the…

View On WordPress
#Carl-Gustaf#Defence#Defence Industrial Complex#Defense#FDI#Foreign Direct Investment#Haryana#India#Industry#Jhajjar#Manufacturing#Manufacturing Facility#Military#Military Industrial Complex#Production#SAAB#SAAB AB#Saab Group#Sweden#Technology#Weapon System
0 notes
Text
DRDO awards 7 defence contracts to startups
DRDO awards 7 new projects to Indian startups: India’s Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has awarded seven new defence projects to private Indian companies, with a particular focus on nurturing micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) and startups. These projects have been awarded to Indian defence startups spread across the country, from Delhi-NCR to Maharashtra to…
#Accord Software & Systems Pvt Ltd#Alohatech Private Limited#contract#Craftlogic Labs Pvt Ltd Data Pattern India Limited#Defence Ministry#defence startups#DRDO#IROV Technologies Pvt Limited#Oxygen 2 Innovation Pvt Ltd#Sagar Defence Engineering#Technology Development Fund
0 notes
Text
India’s DRDO conducts flight trial of Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator
DRDO Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator: India’s apex defence research body, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) Friday successfully conducted the flight trial of the Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator, an indigenously designed and developed flying wing UAV, at the Aeronautical Test Range (ATR) in Chitradurga district in southern state Karnataka. The…

View On WordPress
0 notes